Monthly Economic Trends in South Korea, June 2022

Korea’s economic recovery is losing steam over global supply chain disruptions and surging raw material prices, notwithstanding the recent upturn in the service industry.

With the lifting of social distancing restrictions, the service industry shows signs of recovery led by face-to-face services.
╺ Production made a relatively strong rebound in service businesses, such as accommodation and food services and arts, sports, and recreation-related activities.
╺In addition, employment conditions showed a solid improvement as the number of employed persons continued to increase in the service and manufacturing industries.

However, the manufacturing industry is decelerating on the back of prolonged supply chain disruptions and persistently high raw material prices, bringing down the pace of economic recovery.
╺Export growth is gradually slowing down, reflecting weaker global growth and the adverse impacts of China’s Zero-COVID policy.
╺In April, production in most key manufacturing segments saw a fall from the previous month, with stagnant equipment investment and limited recovery in durable goods sales.
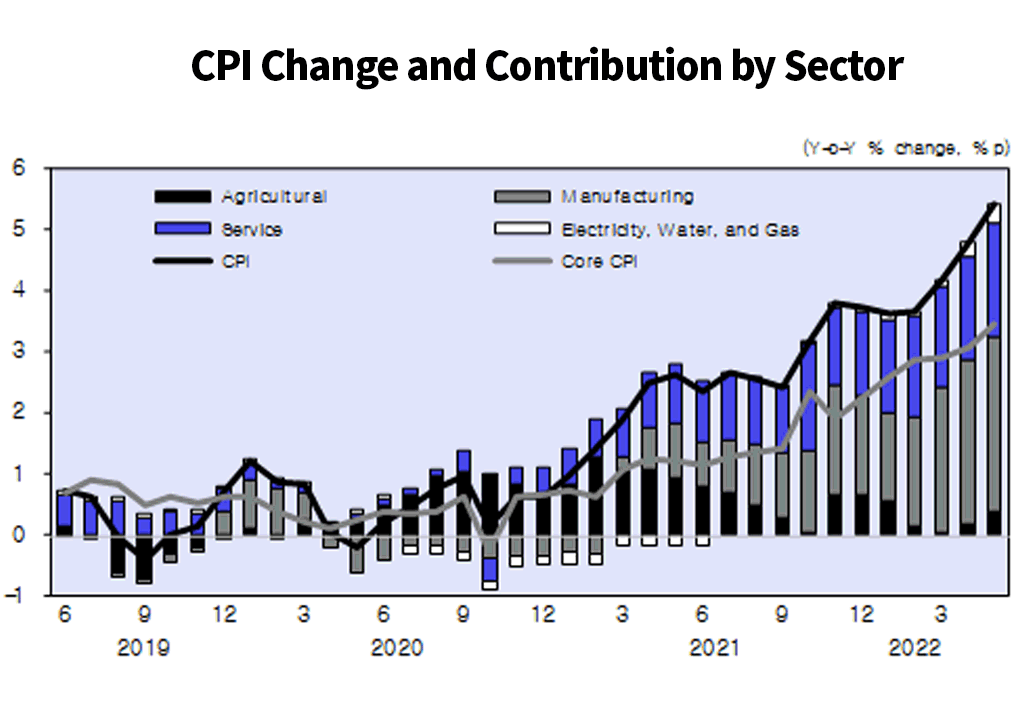
╺High inflation caused by rising raw material prices is hurting the purchasing power of households and firms and pushing up interest rates locally and globally, posing a downside risk to economic activity.



